The Risk Register (Risk Mappings) page allows user to assign risks to the tasks in the project selected. The risks can be of two types; Threat which gives a negative impact to the task, and Opportunity which gives a positive impact to the task. A risk can be assigned to multiple tasks in the project.
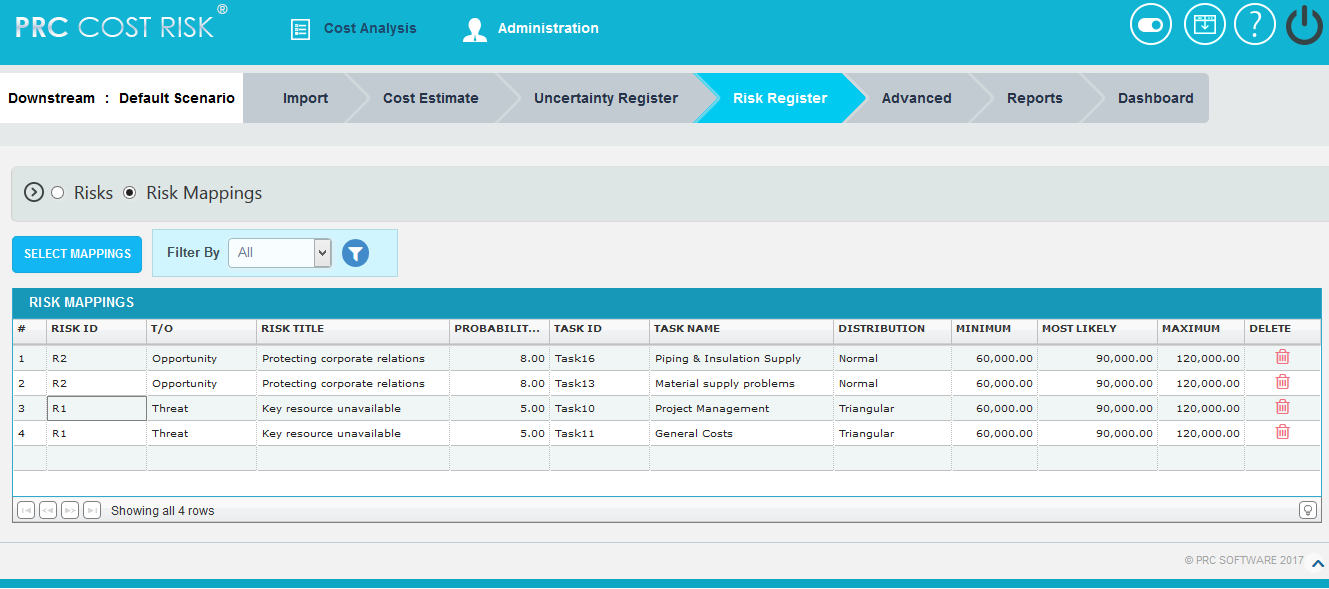
Figure 1
Map Risk to Tasks:
This functionality is used to assign the added risks to tasks.
Steps:
- Risk Register –> Risk Mappings
- Click on the RISK ID column which has to be assigned to the tasks. (Figure 1)
- Check the checkboxes corresponding to the tasks to assign the selected risk. (Figure 2)
- Click on the MAP TASKS button to map the tasks. (Figure 2)
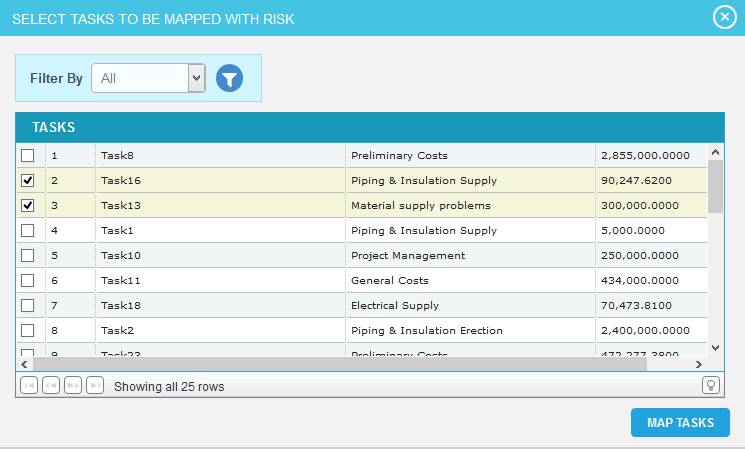
Figure 2
Filter Data:
This functionality is used to filter the data according to a particular field and its selected values for risk / task.
Steps:
- Risk Register –> Risk Mappings
- Select the required column from the Filter by. (Figure 1)
- Enter the value in the textbox provided or select a value from the dropdown based on which filtering is to be done. (Figure 3) While giving conditions with `select multiple´ option to filter, a pop up appears (Figure 4) where the multiple risks can be selected.
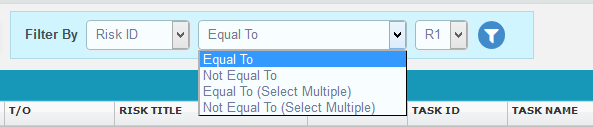
Figure 3
- Click the filter icon (Figure 3). The filtered data will be displayed.
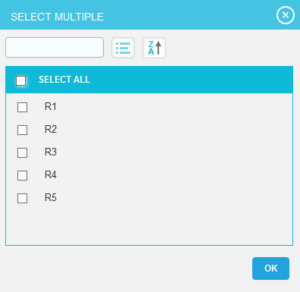
Figure 4
Select Mappings:
This functionality is used to select multiple mappings.
Steps:
- Risk Register –> Risk Mappings
- Click on the SELECT MAPPINGS button. (Figure 1)
- Checkboxes appears on the first column of each mapping which can be check marked for selecting corresponding mappings. (Figure 5)
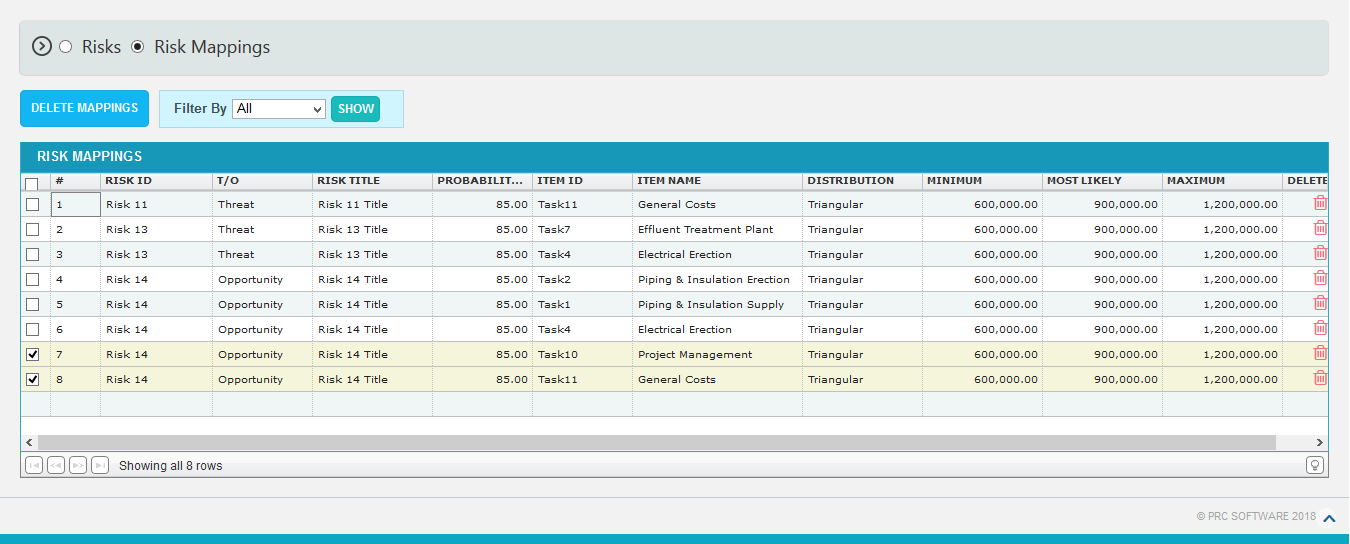
Figure 5
Delete Mappings:
This functionality is used to delete multiple mappings from the project.
Steps:
- Risk Register –> Risk Mappings
- Click on the SELECT MAPPINGS button. (Figure 1)
- Check the checkboxes of the corresponding mappings which are to be deleted. (Figure 5)
- Click on the DELETE MAPPINGS. (Figure 5)
- To delete single risk mappings from the project, click Delete icon corresponding to each risk. (Figure 1)
- A pop up appears. Click OK to delete or click Cancel. (Figure 6)
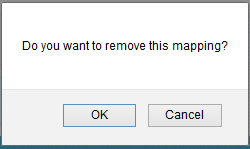
Figure 6